
Tocotrienol & Brain Health
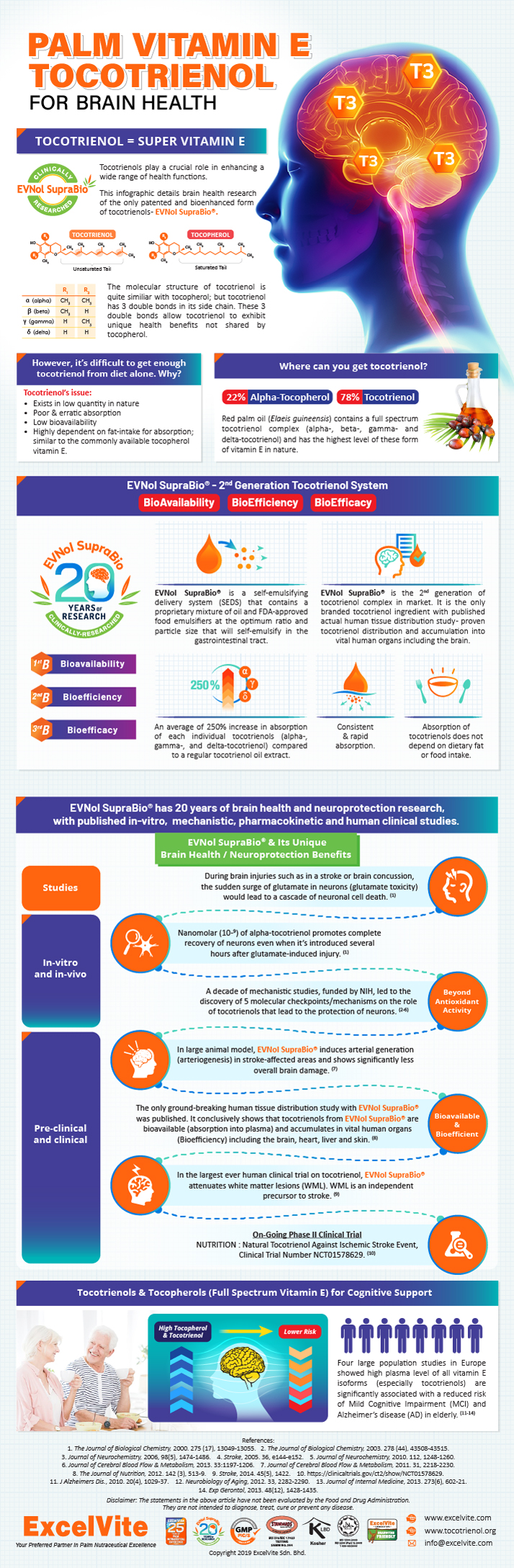
Our Brain acts as a control center that regulates our body biological events such as respiration and metabolism processes. The brain contains high content of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), making it very susceptible to free radical-mediated oxidative stress that negatively affects brain health [1]. When compared to other organs, the brain requires higher amount of oxygen to cater for its metabolic demand [2]. However, this also would lead to higher risk of oxidative stress towards the PUFAs which in turn could damage the neuron. Therefore, lipid soluble antioxidants such as vitamin E (Tocopherols and Tocotrienols) are crucial to minimize oxidative stress and support healthy brain function.
The first neuroprotective action of tocotrienol was reported back in year 2000 where extremely low concentration of alpha-tocotrienol (nanomolar, 10-9) promoted complete recovery of neurons even when alpha-tocotrienol was introduced several hours after the glutamate-induced injury [3]. Interestingly, this benefit was not observed in the commonly-studied alpha-tocopherol. This promising result marked a significant turning point in tocotrienol’s research because researchers and scientists then started to investigate the benefits of tocotrienol in promoting healthy brain function.
Tocotrienol’s research on brain health has moved from in-vitro studies to pre-clinical study and currently, human clinical study; in the span of 20 years. These research studies on brain health were conducted specifically on a full spectrum palm tocotrienol complex called EVNol™ and also on the bioenhanced form of palm tocotrienol complex called EVNol SupraBio™, an oral formulation for softgel dosage form that guarantees at least 2.5 times better tocotrienol absorption in the human digestive system [4].
To celebrate 20 years of full spectrum palm tocotrienol brain health research, a collection of resources will be gradually added to this site/page so that readers will have a better understanding on how this special form of palm vitamin E address important brain health matters.
Please come back every so often to check for updates.
Videos
There is nothing more interesting than getting firsthand information from the researchers who were involved in the studies. Hence, here is a series of videos from an interview session with Prof. Chandan Sen, the lead researcher and pioneer for palm tocotrienol’s brain health research.
Part I : Prof. Chandan Sen reviewed palm tocotrienol’s properties and its potential
Part II : Prof. Chandan Sen discussed palm tocotrienol’s research phases based on FDA’s clinical trial
Part III : Prof. Chandan Sen shared the potential of palm tocotrienol in brain health
Part IV : Prof. Chandan Sen shared the safety and side effect findings of tocotrienol
Part V : Prof. Chandan Sen explained whether tocotrienol can be taken together with Plavix (a blood thinner).
Interview with Prof. Dr. KH Yuen : Neuroprotective Properties of Tocotrienol
In this video, Prof. Yuen first explained the differences between vitamin E tocopherol and tocotrienol. He then moved on to describe the unique neuroprotective properties of tocotrenol (delivery through EVNol SupraBio™) in Pre- and Post-stroke conditions as shown by human clinical studies. Followed by revealing an on-going study that examines the effect of tocotrienol (EVNol SupraBio™) on beta-amyloid induced paralysis in C. elegans, vis-a-vis Parkinson’s Disease.
Infographics
We are delighted to share the infographic below with you that recaps the twenty years of palm tocotrienol brain health research.

More on Brain Health
Craving for more? You are invited to read about the brain research that have been conducted using tocotrienol – ranging from in vitro, animal studies and human clinical studies. Link.
Please feel free to reach out for more details by filling out the form at Contact Us.
References:
- Edem DO: Palm oil: biochemical, physiological, nutritional, hematological, and toxicological aspects: a review. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 57:319–341, 2002.
- Kiple K.F., Ornelas KC: ‘‘The Cambridge World History of Food ’’New York: Cambridge University Press, 2000.
- Sen CK, et al. (2000). Molecular Basis of Vitamin E Action: Tocotrienol potently inhibits glutamate-induced pp60c-Src kinase and death of HT4 neuronal cells. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275 (17), 13049-13055.
- Ho D, et al. (2003). Drug delivery system: formulation for fat soluble drugs. U.S. Patent No. 6,596,306.