Article Source : MPOC
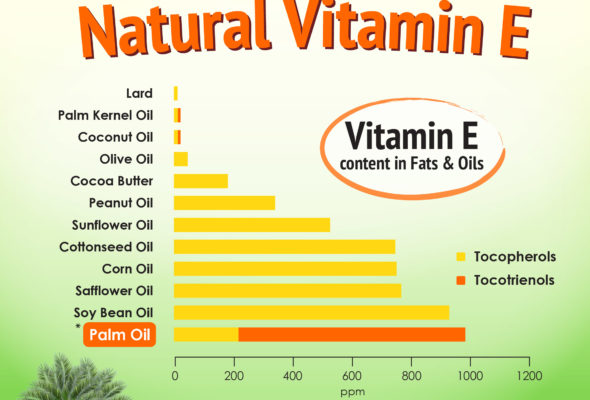
Vitamin E comprised of 2 subgroups namely the Tocotrienols and Tocopherols. Tocopherols are present in common vegetable oils such as soya and corn while tocotrienols are common in cereal grains such as rye (92mg/kg), oat (210mg/kg), rice bran (465mg/kg) and barley (910mg/kg). Tocotrienols are also in abundance in palm oil (940mg/kg). Palm oil also has the highest content of Vitamin E among oils and fats. Several studies have shown shown that tocotrienols possess unique biological properties including higher antioxidant potency and provides greater health benefits than the α-tocopherol form of vitamin E.
During the recently concluded Palm International Nutra-Cosmeceutical Conference (PINC 2017), speakers highlighted recent breakthroughs in palm tocotrienols research and the current clinical practices of using palm tocotrienols for disease management. Some of the highlights are –
1. Tocotrienols for Hair Health
- Studies show inducement of hair growth1
2. Tocotrienols for Neuro Health
- Mixed tocotrienols reduces progression of white matter lesion1
- Palm tocotrienols isoforms helps to reduce NO production by microglia2
- Palm tocotrienols are neuroprotective2
- Palm tocotrienols protect neurons not only via its antioxidative properties but also via anti-inflammatory action2
3. Tocotrienols for Heart Health
- Aids plasma cholesterol reduction in humans’1
- Helps to prevent the formation of atherosclerotic lesions1
- Higher antioxidant potency than α-tocopherol by 40-60 times1
4. Tocotrienols for Peptic Ulcer Therapy
- Reduces oxidative stress that contributes to formation of gastric lesions7
- Tests in animal showed that the degree of peptic ulcer disease is reduced when palm tocotrienols are incorporated into the diet7
- Tocotrienols protects against gastric ulcers disease7
5. Tocotrienols for Bone Health
- Palm tocotrienols demonstrate protective effects against osteoporosis3
- The γ- and δ-tcotrienols are the most effective isomers in maintaining bone structure and strength3
- Improves bone volume and thickness and reduces bone porosity3
6. Tocotrienols for Muscle Health
- Tocotrienols are beneficial for ameliorating muscle degeneration in aging or muscular disease5
- Tocotrienols differ structurally from tocopherols which enables them to penetrate membranes easily and exert a more potent antioxidant effect than tocopherols5
- Tocotrienols facilitate membrane repair by enabling the regenerative action of phospholipids, which are major components of cell membranes5
7. Tocotrienols for Prostate Health
- Gamma tocotrienol demonstrated an ability to inhibit cancer cell proliferation in prostate cancer6
- Gamma tocotrienol inhibit growth of prostate cancer stem cells6
8. Tocotrienols for Liver Health
- Showed significant improvement when used in treating Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)1
9. Tocotrienols for Skin Health
- Reduces wrinkling and oxidative stress1
- Provides protection against long wave ultraviolet A (UVA) radiation that causes skin aging1
- Essential ingredient in cosmetics formulations for scar reduction and acceleration of wound healing1
- Increases skin moisture and elasticity1
- Reduces swelling under eyes1
- Promotes radiant skin1
- Induces lower “biological age” in consumers. The higher the Telomere score, the younger the cells are.1
10. Tocotrienols for Immune Health
- Increases the concentration of anti-TT IgG antibody in patients prone to immune dysfunction and auto-immunity disorder1
- Reduces inflammation caused by IL-6 production1
Many animal and human studies show that tocotrienols are useful against inflammation – associated diseases. Besides its function related to its antioxidant properties, tocotrienols also exhibits other biological properties including neuroprotective, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory and cholesterol lowering effects. The potential of tocotrienols is vast and beneficial in many aspects; thus it could ideally be used as a first line therapy and clinical purposes.
References:
1. Bryce Wylde, Consumer Perception And Pick-up: Where We Are At And Where We Should Be. Paper presented at the Palm International Nutra-Cosmeceutical Conference (PINC 2017), 31st July – 1st August 2017, Le Meridien, Putrajaya.
2. Dr. Sharmili Vidyadaran, Tocotrienols and their effects on microglia: implications for brain inflammatory conditions. Paper presented at the Palm International Nutra-Cosmeceutical Conference (PINC 2017), 31st July – 1st August 2017, Le Meridien, Putrajaya.
3. Prof. Dr. Ima Nirwana Soelaiman, Effect of individual tocotrienol isomers on bone cells in a 3D cell culture system. Paper presented at the Palm International Nutra-Cosmeceutical Conference (PINC 2017), 31st July – 1st August 2017, Le Meridien, Putrajaya.
4. Dr. Nur Azlina Mohd. Fahami, Palm Vitamin E: A Potential Therapy for Peptic Ulcer Disease. Paper presented at the Palm International Nutra-Cosmeceutical Conference (PINC 2017), 31st July – 1st August 2017, Le Meridien, Putrajaya.
5. Prof. Dr. Suzana Makpol, Tocotrienool Promotes Myogenic Differentiation in the Prevention of Replicative Senescence of Myoblasts. Paper presented at the Palm International Nutra-Cosmeceutical Conference (PINC 2017), 31st July – 1st August 2017, Le Meridien, Putrajaya.
6. Dr. Patrick Ling , Dissecting the Mechanism Responsible for the Anti-Cancer Stem Cell Properties of Gamma-Tocotrienol. Paper presented at the Palm International Nutra-Cosmeceutical Conference (PINC 2017), 31st July – 1st August 2017, Le Meridien, Putrajaya.

Source : MPOC